Medical Board of California: Investigation, Accusation and Disciplinary Actions Guide
Everyone can make a mistake, but for physicians a mistake or an unjust claim from an unhappy patient or colleague can subject a physician to medical investigation, accusation and disciplinary actions. California’s “Patient’s Right to Know Act” adds mandatory patient disclosures that can significantly amplify the damage of formal accusations and discipline to a medical practice and doctor’s reputation.





CONTENTS
- Board and DCA investigation
- Medical Board of California
- Osteopathic Medical Board
- 6 stages in disciplinary process:
- 1. Complaint or crime reported
- 2. Investigation, interview
- 3. Medical board accusation
- 4. Administrative hearing
- 5. Writ of mandate appeal
- 6. Petition for relief/reinstatement
- Investigation risks for physicians
- Medical board disciplinary actions
- Patient’s Right to Know Act guide
- Criminal reporting requirement
DCA and California Medical Board Investigations
In many cases, physician disciplinary actions begin with something innocuous – perhaps a patient’s record request or letter in the mail requesting basic information. The letter or email may come from the Department of Consumer Affairs (DCA) Division of Investigation, not the Medical Board of California. Many unsuspecting physicians or their office staff may be unaware this indicates a Medical Board investigation.
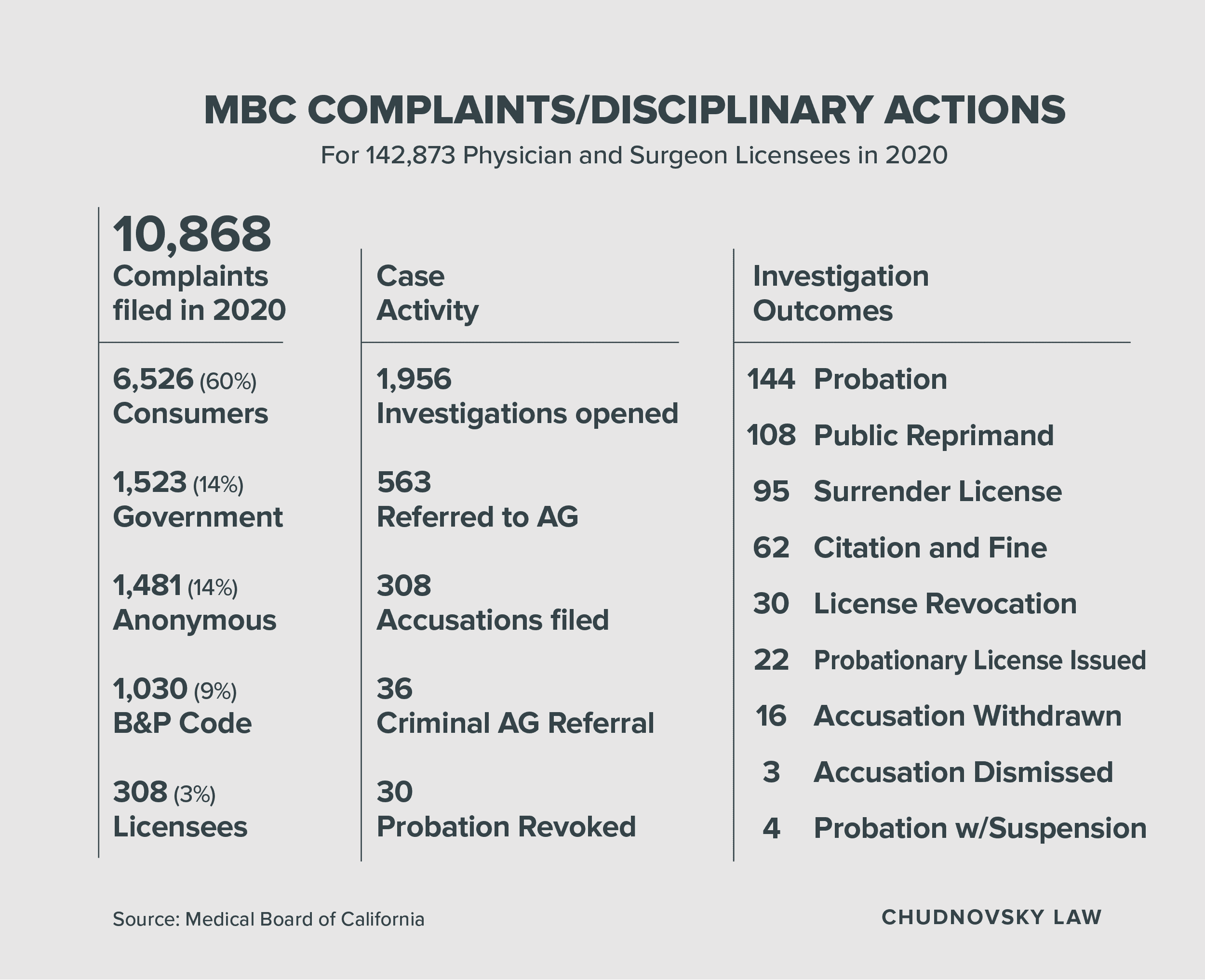
The Medical Board of California received 10,868 complaints in fiscal year 2020 and opened 1,956 investigations. At Chudnovsky Law, we represent California physicians at every disciplinary stage including: pre-investigation analysis, investigation, interviews, accusation defense, hearing, appeal and penalty relief.
Our California medical license defense attorney has published this guide to explain the investigation and discipline process, the risks, and how to protect yourself.
Medical Board of California (MBC)
The Medical Board of California (MBC) licenses and regulates physicians, surgeons and certain health care professionals with the mission to protect health care consumers. The MBC Enforcement Program and Central Complaint Unit (CCU) vigorously investigate complaints, allegations of substandard care, and reports of criminal activity.
California has 152,402 licensed physicians and surgeons, 668 polysomnographic technologists and 460 licensed midwifes as of 2020. The MBC can revoke or suspend licenses or otherwise discipline licensees for violations of the Medical Practice Act.
Medical Board of California
2005 Evergreen Street, Suite 1200, Sacramento, CA 95815
(800) 633-2322 Toll Free | (916) 263-2382 Central complaint unit
mbc.ca.gov
Osteopathic Medical Board of California
The Osteopathic Medical Board of California (OMBC) licenses and regulates osteopathic physicians and surgeons with the mission to protect health care consumers and promote the highest professional standards.
The board investigates consumer complaints and enforces physician compliance with the California Business and Professions Code and Medical Practice Act. California has 11,926 OMBC licensed physicians and surgeons as of 2020.
Osteopathic Medical Board of California
1300 National Drive, Suite #150, Sacramento, CA 95834-1991
(916) 928-8390
ombc.ca.gov

6 Stages in the Medical Board disciplinary process
Even the best physicians can get hit with an unexpected complaint or claim of misconduct when they least expect it. Medical professionals are easy targets for disgruntled patients or others looking to damage a reputation. The most important thing to do is make sure you understand the discipline system, your rights, and when to consult legal counsel.
Unfortunately, once a complaint is filed, you will be caught up in the California Medical Board’s slow, unrelenting process. Unlike in malpractice claims, board actions against physicians are typically based on substandard or unethical conduct that does not require proving actual patient harm.
While some complaints such as fee disputes or inappropriate comments may seem minor, they can grow into different, more severe issues. For example, a records request could reveal a failure to obtain informed patient consent or deficient record keeping. It is, therefore, wise to treat any complaint as a serious matter and respond carefully.
Physician discipline and administrative actions proceed through six stages:
1. Physician Complaint or Crime Reported
Enforcement activity is triggered when the California Medical Board receives:
- A complaint,
- Notification of a criminal charge or conviction,
- An 805 peer review report,
- Notification of a disciplinary action in another state, or
- Other disclosures such as a medical malpractice settlement or award, outpatient surgery center adverse event, coroner report of death due to physician gross negligence, or medical procedure outside of an acute care hospital resulting in patient death.
Complaints can be filed online by anyone, including anonymous parties for alleged violations of the Medical Practice Act. If the Central Complaint Unit analyst review finds that a violation may have occurred that is within the board’s jurisdiction, the complaint will be forwarded to the DCA Division of Investigation for further investigation.
The California Department of Justice sends notification of criminal arrests and convictions to the MBC via CORI notification. When a physician submits an 802 criminal action form to report a criminal arrest or conviction, they can expect an investigation of the matter.
RELATED: Physician criminal reporting requirements
2. Medical Investigation, Interview
The MBC has authority to investigate licensees for a wide variety of complaints. Some of the most common examples include:
- Quality of Care: Substandard care issues, misdiagnosis, negligent care, surgery complications, patient abandonment.
- Office Practices: Deficient record keeping, billing practices, failure to sign death certificate, failure to provide records.
- Unprofessional Conduct: Altering records, breach of confidence, filing fraudulent insurance claims, misleading advertising, arrest or conviction of a crime.
- Provider Impairment. Practicing under the influence of drugs or alcohol, mental or physical impairment.
- Inappropriate Prescribing: Violation of DEA and other drug laws, opioid, excessive/under prescribing.
- Sexual Misconduct.
- Unlicensed Practice or aiding and abetting unlicensed practice.
Physicians usually become aware an investigation has been initiated when they receive:
- Unannounced office visit from an investigator.
- Department of Consumer Affairs Division of Investigation call, request, letter or subpoena for medical or other records.
- Request for an investigator and/or MBC expert reviewer interview.
- Medical Board contact requesting medical or other records.
Medical Board investigators are usually veteran detectives with years of experience in the art of interrogation. They often take a casual, friendly approach that lulls physicians into saying more than they should or releasing information that can cause problems later.
Once a physician becomes aware an investigation has been initiated, it is important to retain a qualified medical license defense attorney with expertise in resolving medical board investigations and license disciplinary matters. Your responses should be reviewed by a lawyer to consider any legal ramifications.
California Medical Board proceedings are very different from medical malpractice litigation – they are handled in different legal venues (Office of Administrative Hearings vs civil court) with different rules, prosecutors, procedures, and statutes of limitations.
MBC investigators conduct investigations that can include:
- Interviewing physicians, witnesses and the complainant.
- Setting up and executing undercover sting operations.
- Draft and execute any needed subpoenas and search warrants.
- Obtain relevant medical and other records.
- Obtain review by an MBC Expert Reviewer.
- Examine the location of the alleged act(s).
Important Note: If your matter is closed in the investigation stage, the allegation against you will not be published on the Medical Board’s website or Breeze.
3. Medical Board Accusation
When an investigation finds evidence that a physician has violated the Medical Practice Act and the violation deserves disciplinary action, the matter is advanced to the Attorney General’s Office. If a Deputy Attorney General believes the legal standard has been met for a violation, a formal accusation will be filed and served on the physician. An accusation is a charging document that lists the alleged violations and the applicable laws.
Once the Attorney General files an accusation, the matter will become public record on the MBC website and Breeze database. A physician has the right to dispute the allegations in a hearing at the Office of Administrative Hearings as long as request for hearing (“notice of defense”) is filed within 15 days of receipt of the accusation (Gov Code Section 11506). Otherwise you will be deemed to have waived your right to a hearing and the board can take action as outlined in the Accusation.
If you have received an Accusation, contact us as soon as possible to review your case and how to protect your license.
ACCUSATION CONSEQUENCES EXPLAINED
4. Hearing at the Office of Administrative Hearings
If your Accusation is not resolved through negotiation with the Deputy Attorney General, then it will be decided via a hearing at the Office of Administrative Hearings (OAH). Administrative hearings are similar to court trials, but are held at four OAH locations in Los Angeles, Oakland, Sacramento or San Diego. The matter is argued in front of an Administrative Judge by your counsel and a Deputy Attorney General.
During the hearing, the burden of proof is on the Deputy Attorney General to prove their case. As Medical Board guidelines state, the standard of proof is “clear and convincing evidence to a reasonable certainty.” This challenging standard is much higher than in civil litigation cases. If “gross negligence,” “repeated negligent acts,” or “substantially-related” conduct is alleged, expert testimony is necessary to prove the violations.
After the hearing, the Administrative Law Judge has 30 days to render a proposed decision. The proposed decision is then sent to a seven-member panel of the California Medical Review Board for consideration. The MBC panel makes a final determination on disciplinary matters and can restrict, revoke, or suspend the medical license; reject the proposed decision, or impose other administrative actions. Licensees can petition the MBC to reconsider the decision for up to 30 days after it is adopted.
Attorneys Robert Weinberg, Gillian Friedman, Brian Bill, Melissa DuChene, and Suzanne Crouts have over 100 years experience defending health care licensees in OAH proceedings, DEA, California courts, and Federal courts for administrative law, licensure, and criminal law matters. They have handled over 8,000 cases and trials and are prepared to vigorously defend you against any allegations.
RELATED: Medical Board decision review guidelines
5. Appeal / Writ of Mandate
A writ of mandate (CCP § 1094.5) is the method of appealing a loss in an administrative hearing. The appeal allows a California Superior Court judge to review the decision to determine if the administrative judge abused their discretion or made errors. Licensees typically have 30 days after the effective date of the decision in order to file a writ of mandate in Superior Court.
6. Petition for Penalty Relief or License Reinstatement
In California, disciplined physicians can file a petition with the Medical Board requesting reinstatement of a revoked license, early termination of probation, or a reduction in disciplinary action penalties. Eligibility rules are complex and there are conditions physicians must demonstrate for a successful outcome.
To learn more about your eligibility and options, call us at (844) 325-1444 to setup a consultation with our experienced attorney.
Medical investigation risks for physicians
Medical Board investigations and accusations can have a devastating effect on a physician’s practice and reputation. Even if you are confident the facts of a matter are in your favor, there are collateral consequences and delays that can affect you professionally. Some examples of risks arising from investigations:
- Prolonged distraction: Complex due process regulations, patient’s rights, and a cumbersome investigative system where cases are handed off to different departments all combine to make investigations proceed at a lethargic pace that can cause stress and distraction.
- Reputation: Even a claim without merit can cause reputational damage due to rumors and public online access to complaints and supporting documents.
- Disclosing to stakeholders: Practice partners, insurance plans, hospital groups and other stakeholders can learn of the investigation. Details can be posted on the Medical Board website, the Federation of State Medical Boards database and the National Practitioners Data Bank.
- Increased insurance cost: Disciplinary actions can cause insurance carriers to refuse insurance or dramatically increase the cost of insurance.
While physicians typically can continue practicing during an investigation, it is critical to consult experienced legal counsel.
Types of physicians more at risk of being disciplined
A study of 890 physicians disciplined by the Medical Board of California conducted by Neal Kohatsu, MD found that:
- Male physicians were nearly three times as likely to be disciplined as females.
- Non-board certified physicians were twice as likely to be disciplined than board-certified physicians.
- Family physicians, general practitioners, gynecologists, obstetricians and psychiatrists were more likely than internists. Pediatricians and radiologists were the least likely.
- Foreign medical school graduates had an increased risk.
- Older physicians had slightly increased risk with age.
A California Research Bureau (CRB) study of racial disparity found that during 2003 to 2013, the rate of MBC disciplinary actions varied widely by physician race:
- Asian doctors were 23% less likely to be disciplined
- White doctors were 7% more likely to be disciplined
- Black doctors were 55% more likely to be disciplined
- Latino doctors were 96% more likely to be disciplined
If you are facing an investigation, call us at (844) 325-1444 as early as possible. Our experienced lawyers will advise you how to best protect yourself and develop an effective defense. Representation by an experienced lawyer can substantially increase the likelihood of resolving your case without disciplinary action.
California Medical Board disciplinary actions
The Medical Board of California implements a wide range of physician disciplinary actions depending on the circumstances. The MBC Manual of Model Disciplinary Orders and Disciplinary Guidelines and the Uniform Standards for Substance-Abusing Licensees define the types of orders that may be implemented and the recommended range of penalties for violations.
While protection of the public is the primary priority for the MBC, BPC § 2229 requires that, whenever possible, board actions should be calculated to aid in rehabilitating the licensee. The board has the authority to consider the facts of each case to support a deviation from their guidelines.
MBC disciplinary orders and optional conditions can include:
- Revocation – Single Cause
- Revocation – Multiple Causes
- Standard Stay Order
- Actual Suspension
- Controlled Substances – Total Restriction
- Controlled Substances – Surrender of DEA Permit
- Controlled Substances – Partial Restriction
- Controlled Substances – Maintain Records and Access To Records & Inventories
- Controlled Substances – Abstain From Use
- Alcohol – Abstain From Use
- Biological Fluid Testing
- Community Service – Free Services
- Education Course
- Prescribing Practices Course
- Medical Record Keeping Course
- Professionalism Program (Ethics Course)
- Professional Boundaries Program
- Clinical Competence Assessment Program
- Written Examination
- Psychiatric Evaluation
- Psychotherapy
- Medical Evaluation and Treatment
- Monitoring – Practice/Billing
- Solo Practice Prohibition
- Third Party Chaperone
- Prohibited Practice
When the MBC orders probation for a physician, the final decision will be transmitted to the Probation Unit office. An inspector will be assigned to monitor the licensee to ensure compliance with the terms of probation. The MBC can issue a cease practice order for physicians not in compliance with certain terms of their probation.

Experienced California medical license lawyers
When your reputation and ability to practice are put at risk, there is no substitute for experience and knowledge of the system and tactics you are facing. Chudnovsky Law attorneys Robert Weinberg, Gillian Friedman, Brian Bill, Melissa DuChene, and Suzanne Crouts have over 100 years experience representing physicians in California Medical Board license defense, federal, DEA and state criminal defense matters.
We invite you to read client testimonials and ratings to learn more about how we have helped other physicians facing medical board disciplinary actions. Our lawyers have the experience to proficiently handle your case and investigators while protecting your rights and medical license.
To learn more and discuss your situation, call us at (844) 325-1444.
Resources:
“Robert Weinberg defended my case with the Medical Board with competence and vigor. He always made sure I was prepared, had a clear strategy, and kept me informed throughout the process. I relied on Robert to handle a high stakes matter for me and he delivered in spades. I would recommend him to other physicians without hesitation. Thanks for representing me Robert.”
RAUN
Licensing Consultation and Analysis
If you would like to book a 1 hour legal analysis and advice session on your license case, please visit the page below.
Disclaimer
This information does not constitute legal advice and is not a substitute for individual case consultation and research. No representations are made as to the accuracy of this information and appropriate legal counsel should be consulted before taking any actions. Contact us for a consultation regarding your case to see if we are the best Medical Board of California license defense attorneys for you.





